AWS Architecture
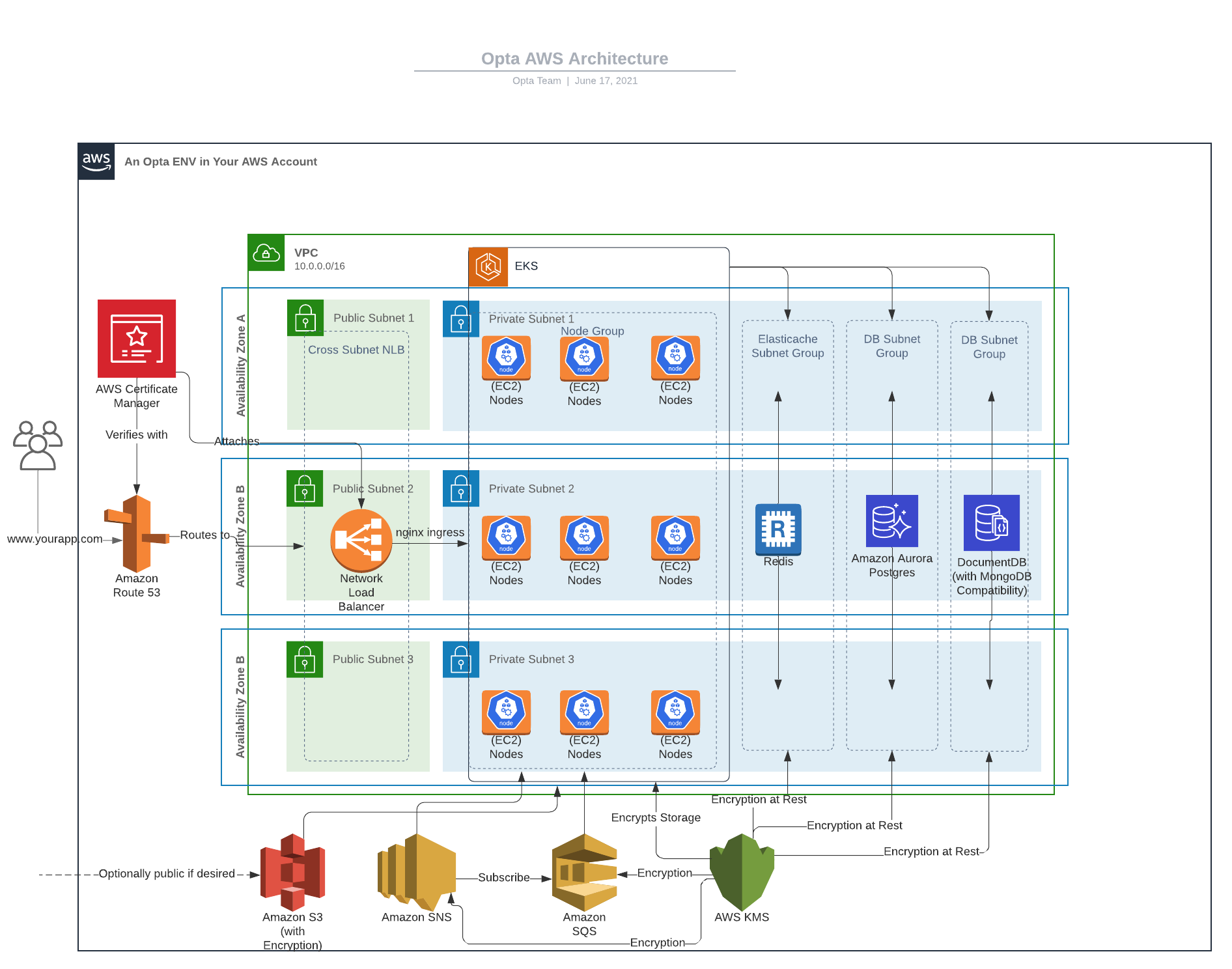
Description
For AWS our environments are currently setup within a single region, but our networking is set up across 3 availability zones by default, split between a private and public subnet (which we provision as we do not use the default vpc). The public subnet is solely used for the public load balancer, while the ec2s (VMs) and databases all exist within the private subnet.
We deploy the EKS cluster with one nodegroup spanning all the private subnets created. The current EKS cluster version is 1.18, but this can be manually overridden if needed (and we get security patches as needed automatically via EKS). Currently, there is a public cluster endpoint, but this may be revisited once a story for VPN support is planned out. Encryption for the secrets is also provided via KMS.
For databases, we currently have modules for postgres (AWS Aurora), redis (AWS Elasticache), and the mongodb compatible
documentdb (AWS Documentdb). We now offer a multi_az option so that read replicas can be created in other az.
The postgres and documentdb databases are built with 5 day retention of backups in case of emergency.
The username and passwords are created with the database and are passed securely to the K8s services as
secrets (pls see K8s section for security around secrets).
There is a module for S3 storage, which creates a private bucket by default (but can be set to public via fields) and all the buckets are encrypted at rest with AES 256 regardless.
There is a module for SQS queues which creates the queue as well as a new kms key with which to encrypt the queue at rest.
There is a module for SNS topics which creates the topic as well as a new kms key with which to encrypt it, and optionally.
To grant access to AWS resources programmatically, a user can use our IAM user/role modules and use the links field to add permissions for the listed resources with the permissions which they specify or the default.
Lastly, DNS and SSL are currently handled via one Route53 hosted zone and one ACM certificate respectively. ACM cert verification is done with Route53 record manipulation in the given hosted zone. Records will be added to the hosted zone directing to the load balancer via an open source integration (see K8s section).
Security Overview
- With linkerd and domain delegation complete, Opta environments will have end-to-end encryption on all Opta services.
- All databases and ec2s are run within the private subnets (i.e. can access the internet via a nat gateway, but nothing external can reach them).
- All databases (redis, documentdb, sql) are encrypted at rest with a KMS key provisioned by the environment.
- All database connections use SSL encryption.
- All S3 buckets are encrypted with AES 256.
- All SQS queues are encrypted at rest, each with a personal KMS key.
- All SNS topics are encrypted at rest, each with a personal KMS key.
- All networking access is managed via security groups either auto-provisioned by EKS, or manually crafted to just expose to the VPC and just the ports required for standard usage (i.e. 5432 for postgres).
- The EKS node ec2s are created with just the AmazonEKSClusterPolicy
- The EKS storage (e.g. K8s secrets) is encrypted at rest via KMS
- K8s service accounts are mapped to IAM roles via the officially sanctioned OIDC manner, with no long-lived credentials.
- No long-lived IAM credentials are ever created.
- All ECR images/repos are private to the account.
- S3 buckets created privately by default.
- 5 day backup retentions for the postgres/documentdb databases.
- Currently, the EKS cluster is built with a public endpoint for the simple usage (can add private option later on once VPN feature is added).
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Glad to hear it! Please tell us how we can improve.
Sorry to hear that. Please tell us how we can improve.